1Q50.30 • Gyroscope
Location: Cabinet 1
Make sure to add a note of which experiment you want when requesting!! Different experiments require different set-ups.
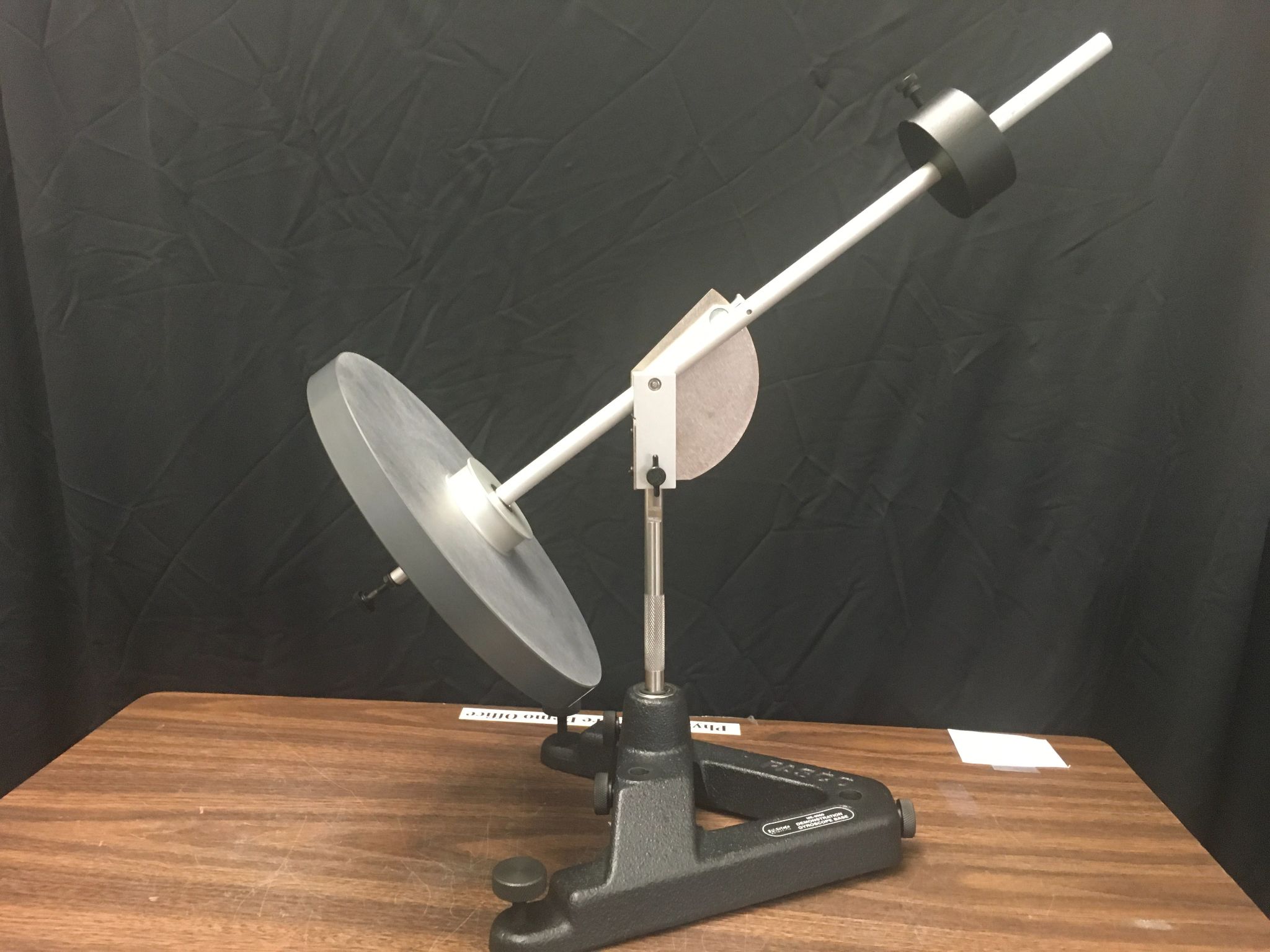
Experiment 1: Weighted
Photo Shows the Demonstration used by the University of Texas at Austin
Faculty Instructions:
- Spin the wheel while holding the bar horizontal to the stand.
- Once spinning, let go of the main horizontal bar.
- The gyroscope should start orbiting horizontally and oscillating vertically (precession).
- Slow or stop the precession by grabbing the center vertical shaft with your hand. As you do, the disk will fall. You can also cause the disk to rise by spinning the center vertical shaft in the same direction as the precession.
Demo Staff Notes:
- You may change the weights to adjust the gyroscope motion for faculty.
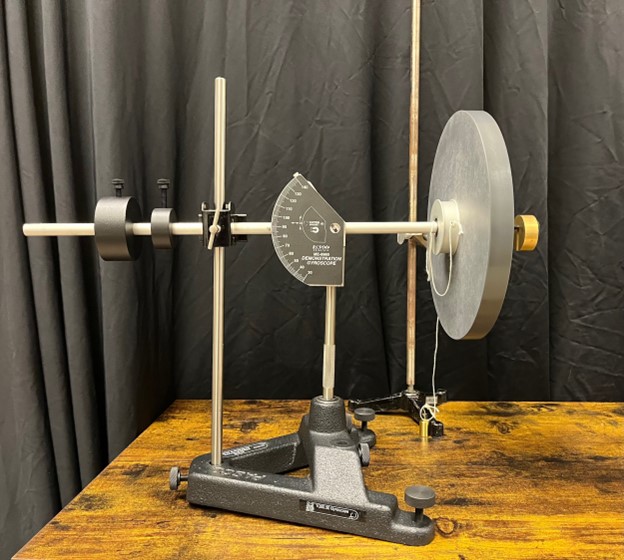
Experiment 2: Nutations
Faculty Instructions:
- Three nutations experiments are listed below. Note that you can release the disk at different angles to see its effect on the nutation.
- Spin the disk and release the gyroscope from rest at an angle of 30 degrees.
- Release the gyroscope from the same angle, but this time giving it an initial push in the direction of precession.
- Release the gyroscope from the same angle, but this time giving it an initial push in the direction opposite of the precession.
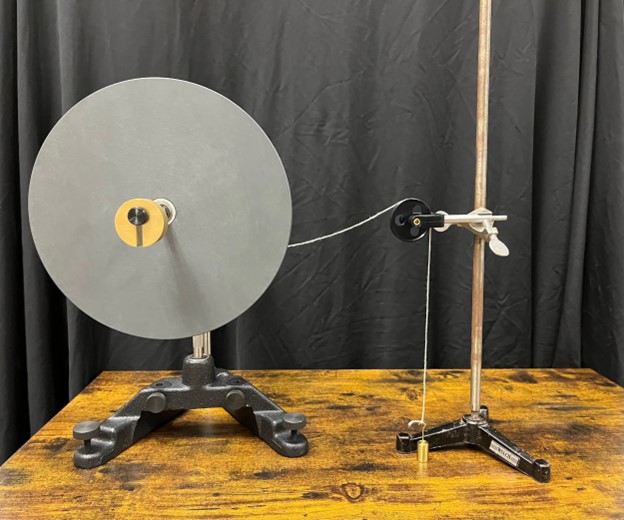
Experiment 3: Measuring Acceleration
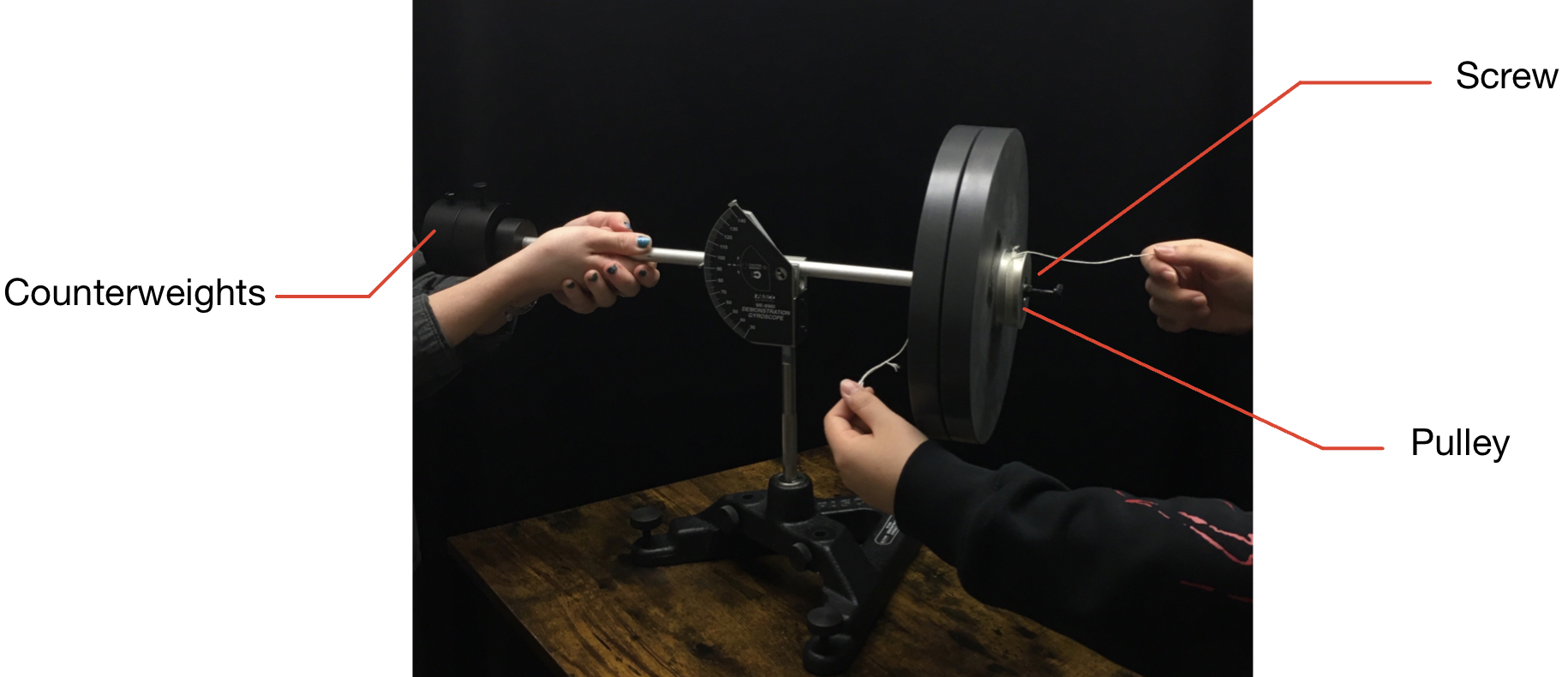
Photo Shows the Demonstration used by the University of Texas at Austin
Faculty Instructions:
- Tightening the string until the mass is close to the black pulley, let go of the string and measure the time it takes for the mass to reach the table from the black pulley.
- Repeat this five times in order to find the acceleration of the disk.
Demo Staff Notes:
- Using the already set up gyroscope, add a metal rod in the last hole on the stand and then clamp it to the horizontal rod using the right angle rod clamp.
- Make sure the vertical and horizontal rod are perpendicular to each other.
- Wind a thread around the pulley on the center shaft of the gyroscope disk, and then pass that over the black pulley, which is connected to an external vertical rod by right angle clamp.
- Attach a 20g mass at the end of the string after it passes over the black pulley.
Experiment 4: Counter-Rotating Disks
Faculty Instructions:
- While holding the horizontal bar at 90 degrees, spin both disks in the same direction to show that the gyroscope does not precess and then let go of the bar.
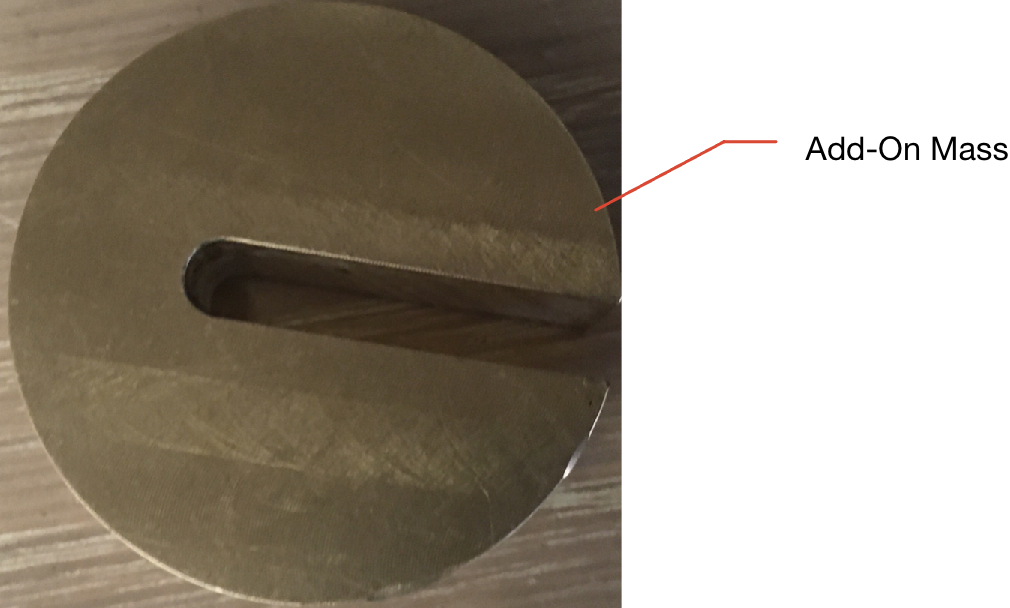
- Put an add-on mass on the screw. Repeat the directions from part 1, this time showing that the gyroscope does precess.
- Stop the disks and reverse their spin to demonstrate precess in the opposite direction.
- To counter-rotate the disks, there should already be strings wrapped around the pulley in opposite directions. Make sure the pins on each pulley are facing
towards the ceiling then pull on both strings simultaneously.
- This will be a 2 person demonstration: one is holding the horizontal bar, and the
other will pull both strings simultaneously. When the person pulling on the strings
stops, the person holding the bar will let go.
- NOTE: if the gyroscope precesses even after you pull on the strings, simply stop its rotational motion by holding and setting the bar at 90 degrees, and then let go. The two disks should naturally want to not precess, demonstrating that counterrotation still does not precess.
- NOTE 2: Even though a torque is still being applied to the gyroscope, the gyroscope does not precess when the two disks are spinning in opposite directions.
- This will be a 2 person demonstration: one is holding the horizontal bar, and the
other will pull both strings simultaneously. When the person pulling on the strings
stops, the person holding the bar will let go.
Demo Staff Notes:
- Remove the screw at the end of the horizontal rod and slide the second disk onto it with the pulley side facing away from the first disk. Secure the second disk by tightening the screw at the end of the rod.
- Put the second counterweight on the other end of the rod and position the counterweights until the gyroscope is balanced. Spin the disks and check the balance by seeing if the gyroscope precesses. If it precesses, the balance needs further adjustment.
- Loop the string over the pins on top of the pulley, and wrap them around the pulley in opposite directions (do this on part 4 of the instructions).
Photo Shows the Demonstration used by the University of Texas at Austin
Concepts Conveyed:
- When torque is applied to two opposite-spinning disks, they will not precess as if they were spinning in the same direction with no torque.
Last updated on February 25, 2025